Page 50 - Year 10 Knowledge Organiser
P. 50
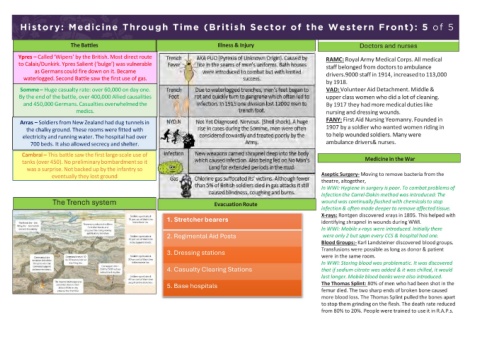
History: Medicine Through Time (British Sector of the Western Front): 5 of 5
The Battles Illness & Injury Doctors and nurses
Ypres – Called ‘Wipers’ by the British. Most direct route RAMC: Royal Army Medical Corps. All medical
to Calais/Dunkirk. Ypres Salient (‘bulge’) was vulnerable staff belonged from doctors to ambulance
as Germanscould fire down on it. Became drivers.9000 staff in 1914, increased to 113,000
waterlogged. Second Battle saw the first use of gas.
by 1918.
Somme– Huge casualty rate: over 60,000 on day one. VAD: Volunteer Aid Detachment. Middle &
By the end of the battle, over 400,000 Allied causalities upper class women who did a lot of cleaning.
and 450,000 Germans.Casualties overwhelmedthe By 1917 they had more medical duties like
medics. nursing and dressing wounds.
Arras – Soldiers from New Zealand had dug tunnels in FANY: First Aid Nursing Yeomanry. Founded in
the chalky ground. These rooms were fitted with 1907 by a soldier who wanted women riding in
electricity and running water. The hospital had over to help wounded soldiers. Many were
700 beds. It also allowed secrecy and shelter. ambulance drivers& nurses.
Cambrai – This battle saw the first large-scale use of
tanks (over 450). No preliminarybombardment so it Medicinein the War
was a surprise. Not backed up by the infantry so
eventually they lost ground Aseptic Surgery- Moving to remove bacteria from the
theatre, altogether,
In WWI: Hygiene in surgery is poor. To combat problems of
infection the Carrel-Dakin method was introduced: The
The Trench system EvacuationRoute wound was continually flushed with chemicals to stop
infection & often made deeper to remove affected tissue.
X-rays: Rontgen discovered xrays in 1895. This helped with
1. Stretcher bearers identifying shrapnel in wounds during WWI.
In WWI: Mobile x-rays were introduced. Initially there
2. Regimental Aid Posts were only 2 but sppn every CCS & hospital had one.
Blood Groups:- Karl Landsteiner discovered blood groups.
3. Dressing stations Transfusions were possible as long as donor & patient
were in the same room.
In WWI: Storing blood was problematic. It was discovered
4. Casualty Clearing Stations that if sodium citrate was added & it was chilled, it would
last longer. Mobile blood banks were also introduced.
5. Base hospitals The Thomas Splint: 80% of men who had been shot in the
femur died. The two sharp ends of broken bone caused
more blood loss. The Thomas Splint pulled the bones apart
to stop them grinding on the flesh. The death rate reduced
from 80% to 20%. People were trained to use it in R.A.P.s.