Page 43 - Year 8 Knowledge Organiser
P. 43
Geography: Population and Migration: 6 of 7 Geography: Energy: 7 of 7
Migration is the movement of people, from one place to another. Energy • Traditionally we get energy Global inequalities in the supply and consumption
from oil, coal and wood. of energy
International migration is when people move from one country (the source) to another country (the host). • Many different sources are
generated by changing Energy
Push factors encourage an individual to Pull factors attract individuals to technology. • The richest 13% of people globally use 50% of the
a place • Used for electricity • world’s energy.
The poorest 13% of people globally use 4% of the
leave a place.. It pushes them out. It pulls them in. production, heating, world’s energy.
transport and for water • Countries import and export energy.
supply (e.g. wells). • Some countries do not have their own sources of
Causes of Poland to UK Migration Consequence for Host Country (UK) Consequences for the Source Country (Poland) • Supports industrialisation energy.
and development.
Poland has always had a culture of mobility. For Polish migrants alone contribute £2.5bn in tax every Poland gains £1bn in remittances which the Polish
example, in the nineteenth century hundreds of year. This provides the government with more tax government can invest in infrastructure and services.
thousands of Polish people migrated to the United to invest in improving services and infrastructure. These remittances reduce the amount the UK
States. government can invest in services and infrastructure.
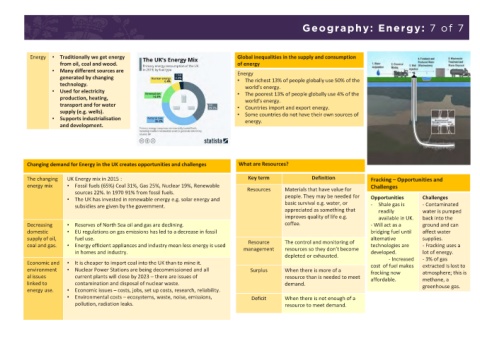
The UK Government offered British citizenship to About 10,500 Poles work in the NHS. These Changing demand for Energy in the UK creates opportunities and challenges What are Resources?
over 200,000 displaced Polish soldiers post WW2. individuals help to treat sick Britons, increasing life
This meant there was already an established Polish expectancies in the UK. The changing UK Energy mix in 2015 : Key term Definition Fracking – Opportunities and
Diaspora in the UK. energy mix • Fossil fuels (65%) Coal 31%, Gas 25%, Nuclear 19%, Renewable Resources Materials that have value for Challenges
sources 22%. In 1970 91% from fossil fuels.
Following the end of communism, Poland had high 80% of migrants are aged between 18 and 35, so • The UK has invested in renewable energy e.g. solar energy and people. They may be needed for Opportunities Challenges
unemployment and low wages. For example, in the UK’s ageing population is counteracted. subsidies are given by the government. basic survival e.g. water, or - Shale gas is - Contaminated
2004, unemployment in Poland was 20% - in the UK it appreciated as something that readily water is pumped
was only 4%. improves quality of life e.g. available in UK. back into the
Decreasing • Reserves of North Sea oil and gas are declining. coffee. - Will act as a ground and can
domestic • EU regulations on gas emissions has led to a decrease in fossil bridging fuel until affect water
In 2004, Poland joined the European Union, giving supply of oil, fuel use. alternative supplies.
Polish people the legal right to come, live and work coal and gas. • Energy efficient appliances and industry mean less energy is used Resource The control and monitoring of technologies are - Fracking uses a
in the UK. The UK was one of only three countries in homes and industry. management resources so they don’t become developed. lot of energy.
that allowed these new European union migrants to depleted or exhausted. - Increased - 3% of gas
come and work straight away. Economic and • It is cheaper to import coal into the UK than to mine it. cost of fuel makes extracted is lost to
environment • Nuclear Power Stations are being decommissioned and all Surplus When there is more of a fracking now atmosphere; this is
al issues current plants will close by 2023 – there are issues of resource than is needed to meet affordable. methane, a
linked to contamination and disposal of nuclear waste. demand. greenhouse gas.
energy use. • Economic issues – costs, jobs, set up costs, research, reliability.
• Environmental costs – ecosystems, waste, noise, emissions, Deficit When there is not enough of a
pollution, radiation leaks. resource to meet demand.