Page 30 - Year 8
P. 30
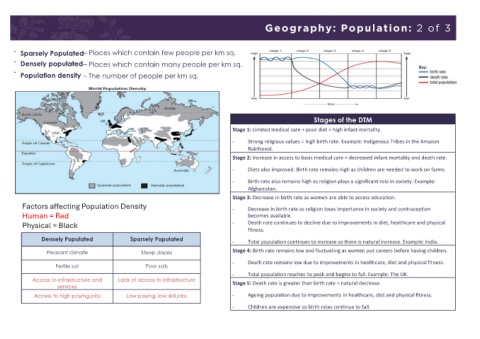
Geography: Population: 2 of 3
• Sparsely Populated– Places which contain few people per km sq.
• Densely populated– Places which contain many people per km sq.
•
Population density – The number of people per km sq.
Stages of the DTM
Stage 1: Limited medical care + poor diet = high infant mortality.
• Strong religious values = high birth rate. Example: Indigenous Tribes in the Amazon
Rainforest.
Stage 2: Increase in access to basic medical care = decreased infant mortality and death rate.
• Diets also improved. Birth rate remains high as children are needed to work on farms.
• Birth rate also remains high as religion plays a significant role in society. Example:
Afghanistan.
Stage 3: Decrease in birth rate as women are able to access education.
Factors affecting Population Density • Decrease in birth rate as religion loses importance in society and contraception
Human = Red becomes available.
Physical = Black • Death rate continues to decline due to improvements in diet, healthcare and physical
fitness.
Densely Populated Sparsely Populated
• Total population continues to increase as there is natural increase. Example: India.
Pleasant climate Steep slopes Stage 4: Birth rate remains low and fluctuating as women put careers before having children.
Fertile soil Poor soils • Death rate remains low due to improvements in healthcare, diet and physical fitness.
• Total population reaches its peak and begins to fall. Example: The UK.
Access to infrastructure and Lack of access to infrastructure Stage 5: Death rate is greater than birth rate = natural decrease.
services
Access to high paying jobs Low paying, low skill jobs • Ageing population due to improvements in healthcare, diet and physical fitness.
• Children are expensive so birth rates continue to fall.