Page 31 - Year 8
P. 31
Geography: Population: 2 of 3 Geography: Population: 3 of 3
• Sparsely Populated– Places which contain few people per km sq. Population structure means the number / proportion of people in each age range, for each gender. Population pyramids show the population
• Densely populated– Places which contain many people per km sq. structure of the country they represent.
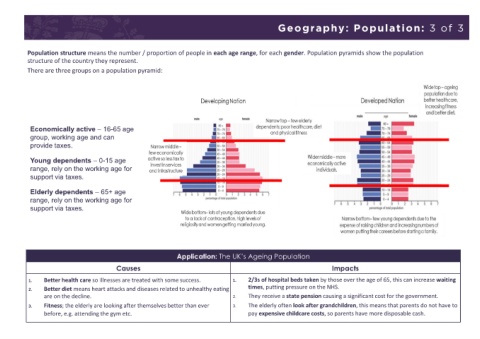
• There are three groups on a population pyramid:
Population density – The number of people per km sq.
Stages of the DTM
Stage 1: Limited medical care + poor diet = high infant mortality. Economically active – 16-65 age
group, working age and can
• Strong religious values = high birth rate. Example: Indigenous Tribes in the Amazon provide taxes.
Rainforest.
Stage 2: Increase in access to basic medical care = decreased infant mortality and death rate. Young dependents – 0-15 age
• Diets also improved. Birth rate remains high as children are needed to work on farms. range, rely on the working age for
support via taxes.
• Birth rate also remains high as religion plays a significant role in society. Example:
Afghanistan. Elderly dependents – 65+ age
Stage 3: Decrease in birth rate as women are able to access education. range, rely on the working age for
Factors affecting Population Density • Decrease in birth rate as religion loses importance in society and contraception support via taxes.
Human = Red becomes available.
Physical = Black • Death rate continues to decline due to improvements in diet, healthcare and physical
fitness.
Densely Populated Sparsely Populated
• Total population continues to increase as there is natural increase. Example: India.
Pleasant climate Steep slopes Stage 4: Birth rate remains low and fluctuating as women put careers before having children. Application: The UK’s Ageing Population
Fertile soil Poor soils • Death rate remains low due to improvements in healthcare, diet and physical fitness. Causes Impacts
• Total population reaches its peak and begins to fall. Example: The UK.
Access to infrastructure and Lack of access to infrastructure Stage 5: Death rate is greater than birth rate = natural decrease. 1. Better health care so illnesses are treated with some success. 1. 2/3s of hospital beds taken by those over the age of 65, this can increase waiting
services 2. Better diet means heart attacks and diseases related to unhealthy eating times, putting pressure on the NHS.
Access to high paying jobs Low paying, low skill jobs • Ageing population due to improvements in healthcare, diet and physical fitness. are on the decline. 2. They receive a state pension causing a significant cost for the government.
• Children are expensive so birth rates continue to fall. 3. Fitness; the elderly are looking after themselves better than ever 3. The elderly often look after grandchildren, this means that parents do not have to
before, e.g. attending the gym etc. pay expensive childcare costs, so parents have more disposable cash.