Page 33 - Year 8
P. 33
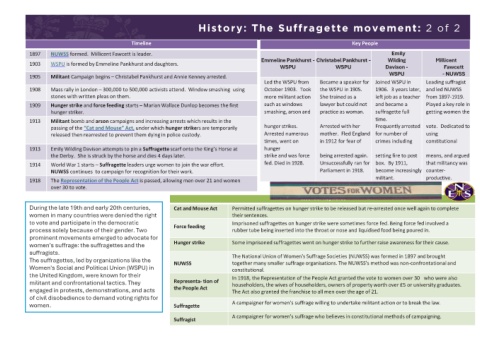
History: WW1: 1 of 2 History: The Suffragette movement: 2 of 2
Timeline Key People
Keywords: 1897 NUWSS formed. Millicent Fawcett is leader. Emily
Word War One: A global conflict involving the main European Powers and their empires from August 1903 WSPU is formed by Emmeline Pankhurst and daughters. Emmeline Pankhurst - Christabel Pankhurst - Wilding Millicent
1914 to November 1918. WSPU WSPU Davison - Fawcett
Long term cause: Factors/causes which happen a long time before an event takes place. 1905 Militant Campaign begins – Christabel Pankhurst and Annie Kenney arrested. WSPU - NUWSS
Short term cause: Factors/causes which happen just before an event takes place – usually a catalyst. Led the WSPU from Became a speaker for Joined WSPU in Leading suffragist
Militarism: An emphasis on military ideals and strength. Wanting your country to have a strong army 1908 Mass rally in London – 300,000 to 500,000 activists attend. Window smashing using October 1903. Took the WSPU in 1905. 1906. 3 years later, and led NUWSS
and navy. stones with written pleas on them. more militant action She trained as a left job as a teacher from 1897-1919.
Alliances: A group of countries who promise to support and protect each other. Rival groups have 1909 Hunger strike and force feeding starts – Marian Wallace Dunlop becomes the first such as windows lawyer but could not and became a Played a key role in
rival alliances. hunger striker. smashing, arson and practice as woman. suffragette full getting women the
Imperialism: The desire to conquer colonies, especially in Africa. This brought the powers in conflict: 1913 Militant bomb and arson campaigns and increasing arrests which results in the time.
Germany wanted an empire. France and Britain already had empires. passing of the “Cat and Mouse” Act, under which hunger strikers are temporarily hunger strikes. Arrested with her Frequently arrested vote. Dedicated to
Nationalism: The belief that your country is better than others. This made nations assertive and released then rearrested to prevent them dying in police custody. Arrested numerous mother. Fled England for number of using
aggressive. times, went on in 1912 for fear of crimes including constitutional
Triple Entente: Alliance between Great Britain, France and Russia. 1913 Emily Wilding Davison attempts to pin a Suffragette scarf onto the King’s Horse at hunger
Triple Alliance: Alliance between Germany, Italy and Austria-Hungary. the Derby. She is struck by the horse and dies 4 days later. strike and was force being arrested again. setting fire to post means, and argued
Western Front: Zone of fighting where Germany engaged armies to its west in WWI. 1914 World War 1 starts – Suffragette leaders urge women to join the war effort. fed. Died in 1928. Unsuccessfully ran for box. By 1911, that militancy was
Trench Warfare: Is a type of land warfare using occupied fighting lines consisting largely of trenches, NUWSS continues to campaign for recognition for their work. Parliament in 1918. become increasingly counter-
in which troops are significantly protected from the enemy's small arms fire and are substantially militant. productive.
sheltered from artillery. 1918 The Representation of the People Act is passed, allowing men over 21 and women
Prussia: Was a major military and economic power in Central Europe during the 18th and 19th over 30 to vote.
centuries. Prussia included half of modern Poland and all but southern Germany. Essential Keywords
During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Cat and Mouse Act Permitted suffragettes on hunger strike to be released but re-arrested once well again to complete
women in many countries were denied the right their sentences.
Key individuals: to vote and participate in the democratic Force feeding Imprisoned suffragettes on hunger strike were sometimes force fed. Being force fed involved a
Archduke Franz Ferdinand: Next in line to be ruler of Austria-Hungarian Empire. process solely because of their gender. Two rubber tube being inserted into the throat or nose and liquidised food being poured in.
Assassinated in 1914 in Bosnia. prominent movements emerged to advocate for
Field Marshall Moltke: The chief of staff of the Prussian Army for thirty years, he is women's suffrage: the suffragettes and the Hunger strike Some imprisoned suffragettes went on hunger strike to further raise awareness for their cause.
regarded as the suffragists.
creator of a new, more modern method of directing armies in the field. The suffragettes, led by organizations like the The National Union of Women's Suffrage Societies (NUWSS) was formed in 1897 and brought
Gavrillo Princip: Serbian Nationalist. Member of Black Hand. Assassinated Archduke Women's Social and Political Union (WSPU) in NUWSS together many smaller suffrage organisations. The NUWSS's method was non-confrontationaland
Franz Ferdinand. the United Kingdom, were known for their constitutional.
King George V: King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of militant and confrontational tactics. They Representa- tion of In 1918, the Representation of the People Act granted the vote to women over 30 who were also
India 1910 - 1936. the People Act householders, the wives of householders, owners of property worth over £5 or university graduates.
Tsar Nicholas II: Leader of Russia 1894 - 1917 engaged in protests, demonstrations, and acts The Act also granted the franchise to all men over the age of 21.
Kaiser Wilhelm II: Emperor of Germany, 1888 - 1918 of civil disobedience to demand voting rights for A campaigner for women's suffrage willing to undertake militant action or to break the law.
Alfred von Schlieffen: Creator of the plan for German invasion of France through women. Suffragette
Belgium. A campaigner for women's suffrage who believes in constitutional methods of campaigning.
Suffragist