Page 35 - Year 10 Knowledge Organiser
P. 35
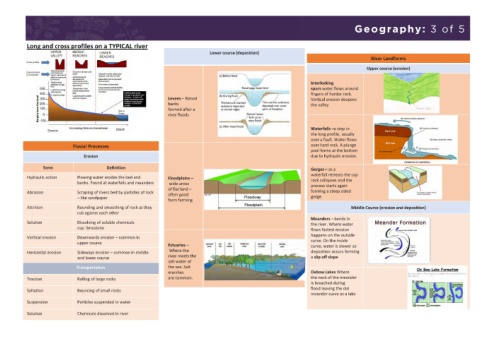
Geography: 2 of 5 Geography: 3 of 5
Coastal Management Strategies Lower course (deposition)
Landforms of deposition Hard Engineering River Landforms
Strategy Benefits Costs Upper course (erosion)
Sand dunes
Sea wall – concrete • V effective • £5000 - £10000 / metre
structure at top of beach • Can develop top for • V expensive Interlocking
acts as a barrier to sea walking, stalls etc • Ugly spurs water flows around
fingers of harder rock.
Rock Armour – large • Relatively effective at • £2000 000 / 100 metres Levees – Raised Vertical erosion deepens
boulders at foot of cliff to reducing force of waves • Ugly banks the valley
reduce force of waves • Relatively cheap • Can be dangerous to public formed after a
river floods
Gabions – wire cages • Flexible • Not attractive
filled with rocks. • Cheaper £50 000 / 100 • Cages can break Waterfalls –a step in
Permeable so metres • Need replacing every 10 years the long profile, usually
improve cliff drainage • Quick to construct
over a fault. Water flows
Spits Groynes – wooden or • Create wider beaches • Starve beaches further Fluvial Processes over hard rock. A plunge
stone fences built at right • Cheap down the coast making pool forms at the bottom
angles to coast to stop them narrower and so more Erosion due to hydraulic erosion.
longshore drift likely to erode
• Need some maintenance Term Definition Gorges – as a
waterfall retreats the cap
Soft Engineering Hydraulic action Flowing water erodes the bed and Floodplains – rock collapses and the
banks. Found at waterfalls and meanders wide areas
Beach nourishment / repr • Looks natural • £50 000 / 100 metres but of flat land – process starts again
forming a steep sided
ofiling. Adding sand to • Creates amenity for can vary Abrasion Scraping of rivers bed by particles of rock often good gorge
a beach or changing its tourism • Needs constant maintenance – like sandpaper form farming
shape eg high ridges • Cheap • Less effective than Attrition Rounding and smoothing of rock as they Middle Course (erosion and deposition)
hard engineering rub against each other
Dune Regeneration • Considered natural • £2000 per 100 metres. Solution Dissolving of soluble chemicals Meanders – bends in
• Creates area for picnics etc Time consuming to plant esp. limestone the river. Where water
• May increase biodiversity and maintain flows fastest erosion
• Easily damaged by storms Vertical erosion Downwards erosion – common in happens on the outside
• Not particularly effective. upper course Estuaries – curve. On the inside
curve, water is slower so
Managed Retreat Horizontal erosion Sideways erosion – common in middle Where the deposition occurs forming
and lower course river meets the a slip off slope
Doing nothing. Allow sea • Long term solution with • Low value land is lost Transportation salt water of
the sea. Salt
to move into area low maintenance to sea marshes Oxbow Lakes Where
• A natural buffer • Local people have to are common. the neck of the meander
• New ecosystem created move so need to Traction Rolling of large rocks is breached during
• Biodiversity be compensated flood leaving the old
improves, eg bird watching • Some ecosystems may Saltation Bouncing of small rocks meander curve as a lake
• More attractive be lost
Suspension Particles suspended in water
Solution Chemicals dissolved in river