Page 34 - Year 10 Knowledge Organiser
P. 34
Geography: 2 of 5
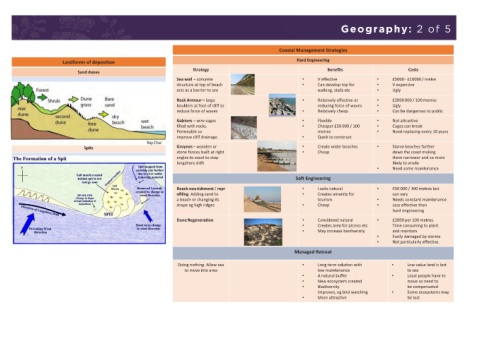
Coastal Management Strategies
Landforms of deposition Hard Engineering
Strategy Benefits Costs
Sand dunes
Sea wall – concrete • V effective • £5000 - £10000 / metre
structure at top of beach • Can develop top for • V expensive
acts as a barrier to sea walking, stalls etc • Ugly
Rock Armour – large • Relatively effective at • £2000 000 / 100 metres
boulders at foot of cliff to reducing force of waves • Ugly
reduce force of waves • Relatively cheap • Can be dangerous to public
Gabions – wire cages • Flexible • Not attractive
filled with rocks. • Cheaper £50 000 / 100 • Cages can break
Permeable so metres • Need replacing every 10 years
improve cliff drainage • Quick to construct
Spits Groynes – wooden or • Create wider beaches • Starve beaches further
stone fences built at right • Cheap down the coast making
angles to coast to stop them narrower and so more
longshore drift likely to erode
• Need some maintenance
Soft Engineering
Beach nourishment / repr • Looks natural • £50 000 / 100 metres but
ofiling. Adding sand to • Creates amenity for can vary
a beach or changing its tourism • Needs constant maintenance
shape eg high ridges • Cheap • Less effective than
hard engineering
Dune Regeneration • Considered natural • £2000 per 100 metres.
• Creates area for picnics etc Time consuming to plant
• May increase biodiversity and maintain
• Easily damaged by storms
• Not particularly effective.
Managed Retreat
Doing nothing. Allow sea • Long term solution with • Low value land is lost
to move into area low maintenance to sea
• A natural buffer • Local people have to
• New ecosystem created move so need to
• Biodiversity be compensated
improves, eg bird watching • Some ecosystems may
• More attractive be lost