Page 39 - Year 10 Knowledge Organiser
P. 39
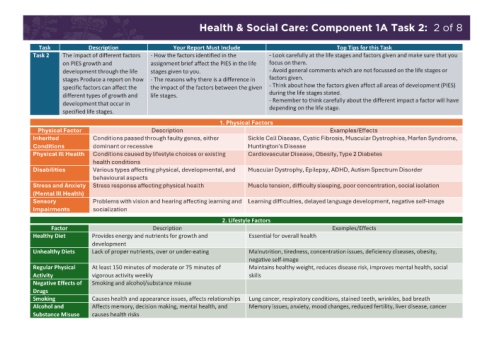
Health & Social Care: Component 1A Task 1: 1 of 8 Health & Social Care: Component 1A Task 2: 2 of 8
Task Description Your Report Must Include Top Tips for this Task
Key Term Definition Task 2 The impact of different factors - How the factors identified in the - Look carefully at the life stages and factors given and make sure that you
Abstract thinking The ability to think about the bigger picture including things that could happen in other scenarios. on PIES growth and assignment brief affect the PIES in the life focus on them.
development through the life stages given to you. - Avoid general comments which are not focussed on the life stages or
Attachment A close two-way emotional bond between infant and carer. stages Produce a report on how - The reasons why there is a difference in factors given.
Bereavement When someone important to us, such as a relative or friend, dies. It is characterised by grief and sadness. specific factors can affect the the impact of the factors between the given - Think about how the factors given affect all areas of development (PIES)
different types of growth and life stages. during the life stages stated.
Fine motor skills Use the small muscles e.g. picking up a pen. development that occur in - Remember to think carefully about the different impact a factor will have
Gross motor skills Use the large muscles e.g. kicking a ball. specified life stages. depending on the life stage.
Language development Children can only begin to speak once they can move and control the muscles in their lips, tongue and larynx.
Infants can understand more words than they can speak. 1. Physical Factors
Physical Factor Description Examples/Effects
Menopause A time in adulthood where physical changes occur in women (approx. 45-55 years). Menopause is reached when Inherited Conditions passed through faulty genes, either Sickle Cell Disease, Cystic Fibrosis, Muscular Dystrophies, Marfan Syndrome,
a woman has not had a period for 12 months. Conditions dominant or recessive Huntington's Disease
Physical Ill Health Conditions caused by lifestyle choices or existing Cardiovascular Disease, Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes
Motor skills Gross motor skills: use the large muscles e.g. kicking a ball. Fine motor skills: use the small muscles e.g. picking health conditions
up a pen. Disabilities Various types affecting physical, developmental, and Muscular Dystrophy, Epilepsy, ADHD, Autism Spectrum Disorder
Perimenopause Perimenopause is when symptoms occur before periods have stopped due to hormone levels fluctuating. This is behavioural aspects
the early stages of menopause. Stress and Anxiety Stress response affecting physical health Muscle tension, difficulty sleeping, poor concentration, social isolation
Primary sexual The physical sexual characteristics that are present from birth and required for reproduction. (Mental Ill Health)
characteristics Sensory Problems with vision and hearing affecting learning and Learning difficulties, delayed language development, negative self-image
Primary socialisation The first learning that takes place in the family. Impairments socialization
Puberty A phase of development where changes occur in the body for males and females. 2. Lifestyle Factors
Factor Description Examples/Effects
Secondary sexual The characteristics that develop during puberty and which are not required for reproduction. Healthy Diet Provides energy and nutrients for growth and Essential for overall health
characteristics development
Secondary socialisation Learning to behave in a way that will help you fit in with society. Unhealthy Diets Lack of proper nutrients, over or under-eating Malnutrition, tiredness, concentration issues, deficiency diseases, obesity,
Self-concept Our idea about ourselves. Consists of two parts: Self-esteem - how you feel about yourself. Self-image - how you negative self-image
see yourself. Regular Physical At least 150 minutes of moderate or 75 minutes of Maintains healthy weight, reduces disease risk, improves mental health, social
Self-esteem How you feel about yourself. Activity vigorous activity weekly skills
Self-image How you see yourself. Negative Effects of Smoking and alcohol/substance misuse
Social play A child plays with other children. Drugs
Solitary play An infant plays on their own. Smoking Causes health and appearance issues, affects relationships Lung cancer, respiratory conditions, stained teeth, wrinkles, bad breath
Alcohol and Affects memory, decision making, mental health, and Memory issues, anxiety, mood changes, reduced fertility, liver disease, cancer
Substance Misuse causes health risks