Page 67 - Year 8 Knowledge Organiser
P. 67
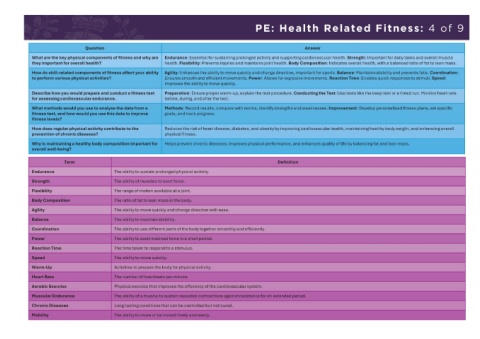
PE: Health Related Fitness: 3 of 9 PE: Health Related Fitness: 4 of 9
Question Answer
HEAD Key Concepts and Knowledge Skills and Applications
What are the key physical components of fitness and why are Endurance: Essential for sustaining prolonged activity and supporting cardiovascular health. Strength: Important for daily tasks and overall muscle
Physical Components of Endurance: The ability to sustain prolonged physical Perform and interpret fitness tests for endurance, strength, they important for overall health? health. Flexibility: Prevents injuries and maintains joint health. Body Composition: Indicates overall health, with a balanced ratio of fat to lean mass.
Fitness activity. Strength: The ability of muscles to exert force. Flexibility: The range of flexibility, and body composition. Develop tailored fitness plans How do skill-related components of fitness affect your ability Agility: Enhances the ability to move quickly and change direction, important for sports. Balance: Maintains stability and prevents falls. Coordination:
motion available at a joint. Body Composition: The ratio of fat to lean mass in to improve these components. to perform various physical activities? Ensures smooth and efficient movements. Power: Allows for explosive movements. Reaction Time: Enables quick responses to stimuli. Speed:
the body. Improves the ability to move quickly.
Describe how you would prepare and conduct a fitness test Preparation: Ensure proper warm-up, explain the test procedure. Conducting the Test: Use tests like the beep test or a timed run. Monitor heart rate
Skill- Agility: The ability to move quickly and change direction with Perform skill-related fitness tests such as agility runs for assessing cardiovascular endurance. before, during, and after the test.
Related Components of ease. Balance: The ability to maintain stability. Coordination: The ability to use and reaction time tests. Develop and refine these skills through
Fitness different parts of the body together smoothly and efficiently. Power: The ability targeted practice and drills. What methods would you use to analyse the data from a Methods: Record results, compare with norms, identify strengths and weaknesses. Improvement: Develop personalised fitness plans, set specific
goals, and track progress.
fitness test, and how would you use this data to improve
to exert maximal force in a short period. Reaction Time: The time taken to fitness levels?
respond to a stimulus. Speed: The ability to move quickly.
How does regular physical activity contribute to the Reduces the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and obesity by improving cardiovascular health, maintaining healthy body weight, and enhancing overall
Fitness Testing Importance of fitness testing to assess current fitness levels and Conduct various fitness tests, record and analyse results, and prevention of chronic diseases? physical fitness.
establish baselines for future improvement. Understanding different fitness use the data to create personalised fitness plans. Reflect on Why is maintaining a healthy body composition important for Helps prevent chronic diseases, improves physical performance, and enhances quality of life by balancing fat and lean mass.
tests and their relevance to overall health. fitness progress and set future goals based on test outcomes. overall well-being?
Long- Understanding how regular physical activity contributes to long-term Reflect on personal fitness goals and their alignment with long- Term Definition
Term Health Benefits health benefits, focusing on cardiovascular health, strength, flexibility, and term health benefits. Discuss and evaluate how different types of
body composition. Recognising how fitness helps prevent chronic diseases physical activity contribute to overall health. Implement Endurance The ability to sustain prolonged physical activity.
and improves quality of life. strategies to incorporate regular physical activity into daily Strength The ability of muscles to exert force.
routines.
Flexibility The range of motion available at a joint.
Healthy Participation Reflection on the long-term health benefits of physical activity. Focus Engage in discussions about the benefits of different fitness Body Composition The ratio of fat to lean mass in the body.
on components of fitness and their impact on overall well-being. components. Evaluate personal fitness levels and identify areas
for improvement. Plan and participate in fitness activities that Agility The ability to move quickly and change direction with ease.
promote long-term health. Balance The ability to maintain stability.
Confidence and Building confidence in participating in new physical activities and Take on leadership roles in fitness activities. Encourage peers Coordination The ability to use different parts of the body together smoothly and efficiently.
Interest developing interest in exploring different sports and activities. and demonstrate enthusiasm for physical activity. Explore new Power The ability to exert maximal force in a short period.
fitness activities and sports.
Reaction Time The time taken to respond to a stimulus.
Application of Techniqu Technique in undertaking fitness tests and physical performance. Perform fitness tests with correct technique. Continuously Speed The ability to move quickly.
es Demonstrating improvement in fitness over time through consistent practice assess and improve fitness levels. Apply learned techniques in
and evaluation. various physical activities and sports. Warm-Up Activities to prepare the body for physical activity.
Heart Rate The number of heartbeats per minute.
Aerobic Exercise Physical exercise that improves the efficiency of the cardiovascular system.
Muscular Endurance The ability of a muscle to sustain repeated contractions against resistance for an extended period.
Chronic Diseases Long-lasting conditions that can be controlled but not cured.
Mobility The ability to move or be moved freely and easily.