Page 55 - Year 11 Knowledge Organiser
P. 55
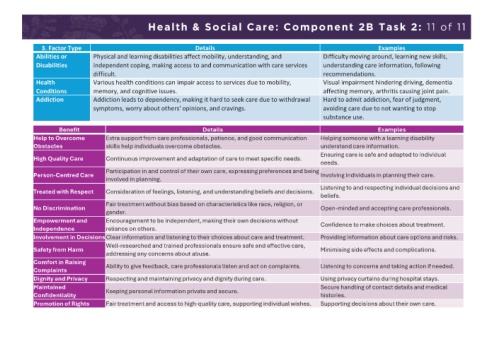
Health & Social Care: Component 2B Task 2: 10 of 11 Health & Social Care: Component 2B Task 2: 11 of 11
Task 2 Your Report Must Include Top Tips for This Task 3. Factor Type Details Examples
Produce a report on how the 1. The potential obstacles that the specified individual 1. Look carefully at which obstacles have been mentioned in the case study Abilities or Physical and learning disabilities affect mobility, understanding, and Difficulty moving around, learning new skills,
skills, attributes and values may have during their care. and focus on them. Disabilities independent coping, making access to and communication with care services understanding care information, following
specified in the case study can 2. How these obstacles might affect their recovery. 2. Avoid general comments which are not focused on the skills, attributes difficult. recommendations.
help the specified individual 3. How the specified skills, attributes and values of the and values given. Health Various health conditions can impair access to services due to mobility, Visual impairment hindering driving, dementia
overcome the obstacles shown. care professionals could help the individual in their 3. Remember to think carefully about how the skills, attributes and values Conditions memory, and cognitive issues. affecting memory, arthritis causing joint pain.
recovery. can help with the individual’s care.
4. Justification for the reasons you have stated. 4. Make sure you give reasons and explanations for your answers. Addiction Addiction leads to dependency, making it hard to seek care due to withdrawal Hard to admit addiction, fear of judgment,
symptoms, worry about others' opinions, and cravings. avoiding care due to not wanting to stop
1. Obstacles Details Examples substance use.
Lack of Time Work and family commitments reduce time and energy for Struggling to find appointment times, reluctance to take time
personal care, making it difficult to follow care plans. off work for treatment. Benefit Details Examples
Lack of Resources Financial constraints and lack of equipment/amenities hinder Inability to afford non-covered services, high transport costs, Help to Overcome Extra support from care professionals, patience, and good communication Helping someone with a learning disability
access to necessary services and adherence to care advice. lack of necessary equipment. Obstacles skills help individuals overcome obstacles. understand care information.
Unachievable Unrealistic or unsuitable targets can demotivate individuals and Unrealistic weight loss goals, unsuitable exercise plans. High Quality Care Continuous improvement and adaptation of care to meet specific needs. Ensuring care is safe and adapted to individual
needs.
Targets make it hard to track progress effectively. Participation in and control of their own care, expressing preferences and being
Lack of Support Insufficient support from family and friends affects Difficulty getting to appointments, lack of someone to talk to Person-Centred Care involved in planning. Involving individuals in planning their care.
transportation, childcare, emotional support, and overall about worries, lack of encouragement to continue care. Listening to and respecting individual decisions and
adherence to care. Treated with Respect Consideration of feelings, listening, and understanding beliefs and decisions. beliefs.
Fair treatment without bias based on characteristics like race, religion, or
No Discrimination Open-minded and accepting care professionals.
2. Obstacle Type Details Examples gender.
Lack of Motivation Difficulty in starting or continuing care due to finding it hard or time- Not making or following up on appointments, not Empowerment and Encouragement to be independent, making their own decisions without Confidence to make choices about treatment.
consuming, impacting appointments and follow-ups. following care recommendations. Independence reliance on others.
Low Self-Esteem Negative self-view and lack of confidence, leading to avoidance of social Avoiding appointments with new doctors, not Involvement in DecisionsClear information and listening to their choices about care and treatment. Providing information about care options and risks.
situations or new people. trying activities due to fear of failure. Safety from Harm Well-researched and trained professionals ensure safe and effective care, Minimising side effects and complications.
Acceptance of Feeling fine and not seeing the need for lifestyle changes or help, ignoring Not going to care services, ignoring advice Comfort in Raising addressing any concerns about abuse.
Current State professional recommendations. despite conditions like high blood pressure. Complaints Ability to give feedback, care professionals listen and act on complaints. Listening to concerns and taking action if needed.
Stress and Anxiety Stress and anxiety from pressure, leading to avoidance of care due to worry, Avoiding care professionals due to fear of bad Dignity and Privacy Respecting and maintaining privacy and dignity during care. Using privacy curtains during hospital stays.
fear, or social anxiety. news, fear of care settings or treatments. Maintained Secure handling of contact details and medical
Confidentiality Keeping personal information private and secure. histories.
Promotion of Rights Fair treatment and access to high-quality care, supporting individual wishes. Supporting decisions about their own care.