Page 36 - Year 9 Knowledge Organiser
P. 36
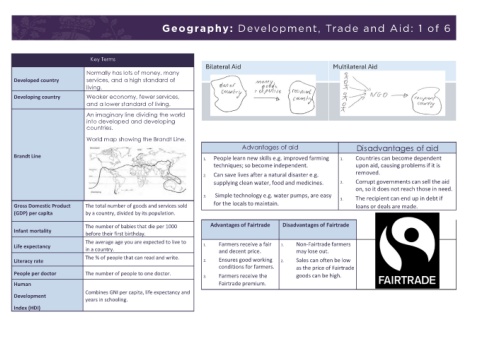
Geography: Development, Trade and Aid: 1 of 6
Key Terms
Bilateral Aid Multilateral Aid
Normally has lots of money, many
Developed country services, and a high standard of
living.
Developing country Weaker economy, fewer services,
and a lower standard of living.
An imaginary line dividing the world
into developed and developing
countries.
World map showing the Brandt Line.
Advantages of aid Disadvantages of aid
Brandt Line
1. People learn new skills e.g. improved farming 1. Countries can become dependent
techniques; so become independent. upon aid, causing problems if it is
2. Can save lives after a natural disaster e.g. removed.
supplying clean water, food and medicines. 2. Corrupt governments can sell the aid
on, so it does not reach those in need.
3. Simple technology e.g. water pumps, are easy 3. The recipient can end up in debt if
Gross Domestic Product The total number of goods and services sold for the locals to maintain. loans or deals are made.
(GDP) per capita by a country, divided by its population.
Infant mortality The number of babies that die per 1000 Advantages of Fairtrade Disadvantages of Fairtrade
before their first birthday.
Life expectancy The average age you are expected to live to 1. Farmers receive a fair 1. Non-Fairtrade farmers
in a country.
and decent price.
may lose out.
Literacy rate The % of people that can read and write. 2. Ensures good working 2. Sales can often be low
conditions for farmers. as the price of Fairtrade
People per doctor The number of people to one doctor.
3. Farmers receive the goods can be high.
Human Fairtrade premium.
Combines GNI per capita, life expectancy and
Development
years in schooling.
Index (HDI)