Page 40 - Year 9 Knowledge Organiser
P. 40
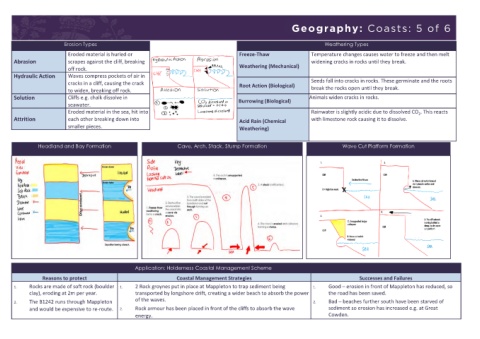
Geography: Coasts: 5 of 6
Erosion Types Weathering Types
Eroded material is hurled or Freeze-Thaw Temperature changes causes water to freeze and then melt
Abrasion scrapes against the cliff, breaking widening cracks in rocks until they break.
off rock. Weathering (Mechanical)
Hydraulic Action Waves compress pockets of air in
cracks in a cliff, causing the crack Root Action (Biological) Seeds fall into cracks in rocks. These germinate and the roots
to widen, breaking off rock. break the rocks open until they break.
Solution Cliffs e.g. chalk dissolve in Burrowing (Biological) Animals widen cracks in rocks.
seawater.
Eroded material in the sea, hit into Rainwater is slightly acidic due to dissolved CO . This reacts
2
Attrition each other breaking down into Acid Rain (Chemical with limestone rock causing it to dissolve.
smaller pieces. Weathering)
Headland and Bay Formation Cave, Arch, Stack, Stump Formation Wave Cut Platform Formation
Application: Holderness Coastal Management Scheme
Reasons to protect Coastal Management Strategies Successes and Failures
1. Rocks are made of soft rock (boulder 1. 2 Rock groynes put in place at Mappleton to trap sediment being 1. Good – erosion in front of Mappleton has reduced, so
clay), eroding at 2m per year. transported by longshore drift, creating a wider beach to absorb the power the road has been saved.
2. The B1242 runs through Mappleton of the waves. 2. Bad – beaches further south have been starved of
and would be expensive to re-route. 2. Rock armour has been placed in front of the cliffs to absorb the wave sediment so erosion has increased e.g. at Great
energy. Cowden.