Page 43 - Year 9 Knowledge Organiser
P. 43
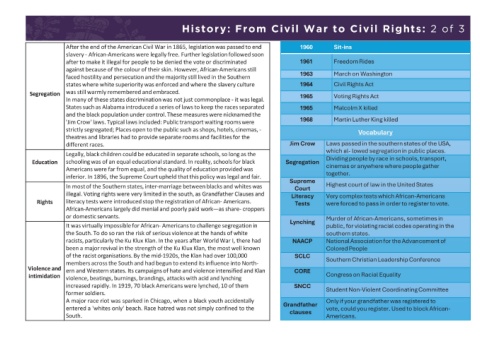
History: The USA in the 'Roaring 20s and 30s’: 1 of 3 History: From Civil War to Civil Rights: 2 of 3
Key Terms The Al Capone Story After the end of the American Civil War in 1865, legislationwas passed to end 1960 Sit-ins
Economic Boom Al Capone has become one of the most slavery - African-Americans were legally free. Further legislation followedsoon
th
majority of businesses infamous individuals of the 20 Century. after to make it illegal for people to be denied the vote or discriminated 1961 Freedom Rides
The son of immigrants, he established
are doing well, sales are himself at a very young age as a gangster. against because of the colour of their skin. However, African-Americans still
high, wages increase and By the age of 20 he had already had a faced hostility and persecution and the majoritystill lived in the Southern 1963 March on Washington
unemployment is low. Consequences of Prohibition number of jobs, committed various
Consumer Society violent crimes, been a member of a states where white superiority was enforced and where the slavery culture 1964 Civil Rights Act
a society where the January 1920, a new law was introduced in America. Prohibition – officially known as the 18 th notorious New York gang and had moved Segregation was still warmly remembered and embraced.
buying and selling of Amendment to the Constitution – outlawed the making, selling or transporting of any drink to Chicago to work for a widely feared In many of these states discrimination was not just commonplace - it was legal. 1965 Voting Rights Act
goods is the most containing alcohol. gang boss. But was he really all that bad?
important activity. Stock The Impact on Society Playing the Stock Market Many thousands of people worked for Al States such as Alabama introduced a series of laws to keep the races separated 1965 Malcolm X killed
Market Prohibition ever worked because people still wanted to drink. They were prepared to break the Capone and many thousands more and the black populationunder control. These measures were nicknamedthe
Where shares in law they never wanted – the criminal gangs were only too willing to get the alcohol for them. These Shares are small parts of benefited from his acts of charity (such as 'Jim Crow' laws. Typical laws included: Public transport waiting roomswere 1968 Martin Luther King killed
companies are bought gangs ran illegal bars called speakeasies, which sold bootleg alcohol smuggled in from abroad by businesses / companies. opening soup kitchens to provide food
and sold. bootleggers. They also sold moonshine - a home-made spirit that was sometimes so strong it caused These shares are sold on the for the homeless and poor). strictly segregated; Places open to the public such as shops, hotels, cinemas, - Vocabulary
Talkies serious illness. In fact, deaths from alcohol poisoning went up from 98 in 1920 to nearly 800 in Stock Market to investors. theatres and libraries had to provide separate rooms and facilities for the
Movies which had sound. 1926. Speakeasies were hidden away in cellars or private hotel rooms (or behind green doors – a The investor then owns a tiny Al left New York in 1919and moved to different races. Jim Crow Laws passed in the southernstates of the USA,
Jazz secret sign of a speakeasy). In 1920 there only 14,313 arrests for drunkenness; by 1925 this had part of the business. During Chicago, America’s second largest city. A which al- lowed segregationin public places.
type of music from the gone up to 51,361. Similarly, in 1922 there were 494 arrests for drunk driving, but by 1925 this the 1920s‘playing the stock gang boss called ‘Terrible’ Johnny Torrio Legally, black children could be educated in separate schools, so long as the
Southern states typified had gone up to 820. Total arrests for drinking offences nearly tripled between 1920 and 1925. market’ became a national had offered him a job. Torrio and Al soon Education schoolingwas of an equal educationalstandard. In reality, schools for black Segregation Dividing peopleby race in schools, transport,
by its fast tempo, lively The Impact on Organised Crime craze. took over a few of the other gangs. Americans were far from equal, and the quality of educationprovided was cinemas or anywhere where peoplegather
Chicago was perfectfor criminals because
rhythms. Prohibition caused a rise in crime. Gangsters made so much money that they could often bribe or Several million people, not just many policemen, judges and even the together.
Flappers intimidate the police, lawyers and judges to cooperate with them and not prosecute them. They the rich but ordinary mayor tookbribes to ‘look the other inferior. In 1896, the Supreme Court upheld that this policy was legal and fair.
young independent also made money through fixing horse and dog racing, running brothels and racketeering, which was Americans too, bought shares way’. In mostof the Southern states, inter-marriage between blacks and whites was Supreme Highest court of law in the United States
women who wore make- when businessmen and shopkeepers aid money to the gangs to stop them smashing up their in all sorts of companies and Torrio and Al were soon making a fortune Court
up, short dresses and premises. A new phrase was coined to describe this behaviour – organised crime. One gang leader, made money by selling them from bootlegging, racketeering, fixing illegal. Voting rights were very limitedin the south, as Grandfather Clauses and Literacy Very complex tests which African-Americans
socialised without the notorious Al Capone, made $10 million a year from racketeering (£875 million in todays on. They then usually bought horse and dog races and overseeing Rights literacy tests were introduced stop the registrationof African- Americans.
chaperones. money). even more shares with the prostitution. Al liked to show off his Tests were forced to pass in order to register to vote.
profits in the hopes of making
Prohibition With booze illegal, the government was unable tax the sale of alcohol. This amounted to the more money again! In the money and enjoyed being photographed. African-Americans largely did menial and poorly paid work—as share- croppers
18 Amendment: equivalent of $11 billion. Money that would have gone directly to the government in tax revenue 1920speople often bought Everyone knew all of his activities, and he or domestic servants. Murder of African-Americans, sometimes in
th
went to gangsters like Al Capone.
banned the sale, shares with money borrowed was arrested from time to time, but it was It was virtually impossible for African- Americans to challenge segregationin Lynching
production or transport EconomicBoom from banks or with a small impossible to convict him because of his public, for violatingracial codes operatingin the
of any alcoholic drink. deposit of 10%. They would control of the police and the fact that no the South. To do so ran the risk of serious violence at the hands of white southernstates.
Bootlegger The boom didn’t just happen because America largely stayed out of World War I, (isolationism) or because then pay the remaining witnesses ever came forward. This type racists, particularly the Ku Klux Klan. In the years after World War I, there had NAACP National Associationfor the Advancementof
person who America was able to earn lots of money selling goods and loans to Europe. There are 3 key reasons why the amount with the profits they of illegal activity is known as ‘organised been a major revival in the strength of the Ku Klux Klan, the most well known
smuggled illegal boom was possible. made when they sold the crime’ – Al Capone organised his criminal ColoredPeople
alcohol from Help fromthe Republican Government: the Fordney-McCumber Tariff Act which put high taxes on goods entering shares. This method of buying activities like a well run business. He even of the racist organisations. By the mid-1920s, the Klan had over 100,000 SCLC
abroad. the country (making foreign goods more expensive to buy).The government cut taxes paid by rich people and shares was called buying on had an accountant, a business plan, and a members across the South and had begun to extend its influence into North- SouthernChristianLeadershipConference
Speakeasy companies so that they could start more companies and create more jobs. # the margin. This worked well hierarchy in his organisation. Violence and
Illegal/hidden bars Growing Industries and Mass Production:The growth of the motor industry was a massive boost to the American as long as the value of shares On 14 February 1929, Capone intimidation ern and Western states. Its campaigns of hate and violence intensified and Klan CORE Congress on Racial Equality
th
which sold alcohol economy. Before long industries were using assembly lines – where products are built bit by bit by different continued to rise. attempted to get rid of his biggest rival – violence, beatings, burnings, brandings, attackswith acid and lynching
during prohibition. people – to help them mass produce items. In 1920 only 4 million people ‘Bugs’ Moran – and his North Side Gang. increased rapidly. In 1919, 70 black Americans were lynched, 10 of them SNCC
Racketeering New Ways to Buy and Sell: Advertising as we know it was born in the 1920s. Colourful billboards, newspapers and owned shares. By 1929there Dressed as a policemen, two of Al’s Student Non-Violent CoordinatingCommittee
gangsters or magazines urged people to buy the latest gadget ad keep up with their neighbours. People were encouraged to use were 20million, including hitmen shot dead seven members of the former soldiers.
organised crime new ‘by now pay housewives, car workers and gang in the St. A major race riot was sparked in Chicago, when a black youth accidentally Only if your grandfather was registeredto
groups demanded later’ schemes, which meant that buyers could pay for goods in small instalments over a fixed period of time. factory workers as well as the Valentine’s Day Massacre. Moran survived entered a 'whites only' beach. Race hatred was not simply confined to the Grandfather vote, could you register.Used to block African-
money from wealthy upper classes. but soon retired. clauses
businesses. South. Americans.