Page 77 - Year 10 Knowledge Organiser
P. 77
PE: Component 1 Task 1: 3 of 8 PE: Component 1 Task 1: 4 of 8
Keyword Definition Private Sector Sports facilities and programs provided by private organizations for profit,
Provision often offering higher quality services and equipment.
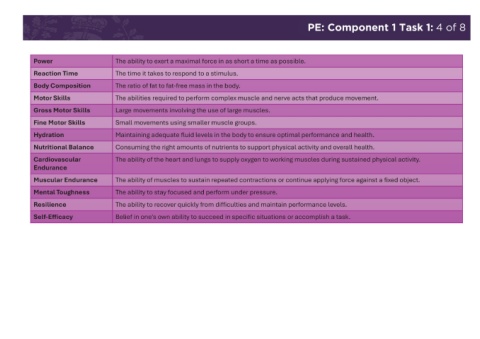
Sport Competitive activity involving physical exertion, with rules and regulations, Power The ability to exert a maximal force in as short a time as possible.
and governed by a National Governing Body. Voluntary Sports facilities and programs run by volunteers or non-profit
Sector organizations, often relying on fundraising and donations.
Team Sport Sports where participants compete with others on a team, such as football, Provision Reaction Time The time it takes to respond to a stimulus.
basketball, and volleyball.
Physical Improvements in physical health, such as increased fitness, better body Body Composition The ratio of fat to fat-free mass in the body.
Individual Sports where participants compete individually, such as tennis, athletics, Benefits composition, and reduced risk of illness, resulting from participation in
Sport and boxing. physical activity. Motor Skills The abilities required to perform complex muscle and nerve acts that produce movement.
Outdoor Adventurous activities done outside or in specialized recreation areas, such Social Improvements in social skills, such as teamwork, leadership, and new Gross Motor Skills Large movements involving the use of large muscles.
Activities as hiking, climbing, and canoeing. Benefits friendships, resulting from participation in physical activity.
Physical Activities aimed at improving fitness, typically involving gym workouts and Mental Improvements in mental health, such as reduced stress, improved mood, Fine Motor Skills Small movements using smaller muscle groups.
Fitness exercises designed to increase strength, endurance, and flexibility. Benefits and increased self-esteem, resulting from participation in physical
Activities activity. Hydration Maintaining adequate fluid levels in the body to ensure optimal performance and health.
National Organizations that govern and regulate sports on a national level, ensuring Intrinsic Motivation driven by internal rewards, such as personal satisfaction or the Nutritional Balance Consuming the right amounts of nutrients to support physical activity and overall health.
Governing rules are followed and promoting the sport. Motivation joy of performing the activity itself.
Bodies (NGBs) Cardiovascular The ability of the heart and lungs to supply oxygen to working muscles during sustained physical activity.
Extrinsic Motivation driven by external rewards, such as trophies, money, or Endurance
Extrinsic An external reward or incentive, such as money, trophies, or certificates, that Motivation recognition.
Motivator motivates individuals to participate in sport or physical activity.
Aerobic The ability to exercise continuously for extended periods without tiring. Muscular Endurance The ability of muscles to sustain repeated contractions or continue applying force against a fixed object.
Cardiorespirat The system that includes the heart and lungs, responsible for the delivery of Endurance
ory System oxygen and nutrients to tissues and the removal of waste products. Mental Toughness The ability to stay focused and perform under pressure.
Anaerobic High-intensity exercise that occurs in short bursts and relies on energy
Musculoskelet The system that includes bones, muscles, and connective tissues, Exercise sources stored in the muscles. Resilience The ability to recover quickly from difficulties and maintain performance levels.
al System responsible for movement and structural support.
Flexibility The ability of muscles and joints to move through their full range of Self-Efficacy Belief in one's own ability to succeed in specific situations or accomplish a task.
Pulse Raiser Activities that gradually increase heart rate to prepare the body for more motion.
intense physical activity.
Strength The ability of muscles to exert force.
Mobilizer Exercises that increase the range of motion in joints and warm up muscles
before physical activity. Coordination The ability to use different parts of the body together smoothly and
efficiently.
Preparation Stretching exercises performed before physical activity to increase flexibility
Stretches and reduce the risk of injury. Balance The ability to maintain the body's position, whether moving or stationary.
Benefits of Positive outcomes of engaging in sport and physical activity, including Speed The ability to move quickly across the ground or move limbs rapidly.
Participation improved fitness, mental health, social skills, and physical health. Agility The ability to change direction quickly and control the movement of the
Barriers to Factors that prevent or hinder individuals from engaging in sport or physical whole body.
Participation activity, such as cost, access, time, and personal or cultural issues.
Public Sector Sports facilities and programs provided by government or local authorities,
Provision often with the aim of making sport accessible to all.